Diseases January 20th, 2025
Gastritis
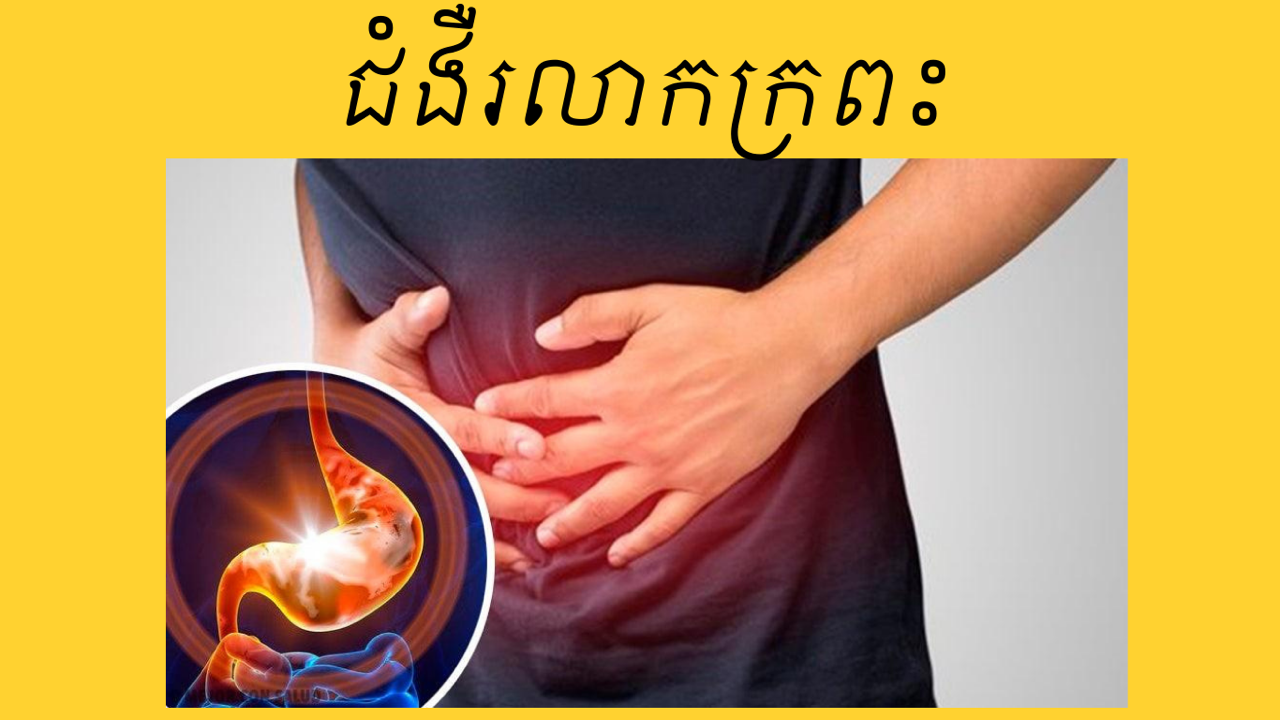
Gastritis is a condition characterized by inflammation, irritation, or erosion of the stomach lining. It can occur suddenly (acute gastritis) or develop gradually over time (chronic gastritis). Gastritis can be caused by various factors, including infections, medications, and lifestyle habits. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding, treating, and managing gastritis:
Symptoms of Gastritis
- Upper abdominal pain or discomfort(burning, gnawing, or aching).
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Bloating or a feeling of fullness in the upper abdomen.
- Loss of appetite.
- Indigestion or heartburn.
- Black, tarry stools (indicating bleeding in the stomach).
- Vomiting blood (in severe cases).
Causes of Gastritis
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) Infection:
- A common bacterial infection that damages the stomach lining.
- Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen.
- Corticosteroids: Can increase stomach acid production.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption:
- Irritates and erodes the stomach lining.
- Stress:
- Severe physical stress (e.g., surgery, burns, or critical illness) can cause acute gastritis.
- Autoimmune Disorders:
- The immune system attacks the stomach lining (autoimmune gastritis).
- Bile Reflux:
- Backflow of bile into the stomach.
- Other Causes:
- Smoking, spicy foods, or a high-fat diet.
Diagnosis
- Medical History and Physical Exam:
- Your doctor will ask about symptoms, medications, and lifestyle habits.
- Tests:
- Endoscopy: A camera is used to examine the stomach lining and take biopsies.
- H. pylori Testing: Breath, blood, stool, or biopsy tests to detect the bacteria.
- Blood Tests: Check for anemia or autoimmune conditions.
- Stool Test: Detect blood in the stool.
Treatment of Gastritis
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. Here are the main approaches:
1. Medications
- Antacids: Neutralize stomach acid (e.g., Tums, Maalox).
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Reduce acid production (e.g., omeprazole, pantoprazole).
- H2 Blockers: Decrease acid production (e.g., ranitidine, famotidine).
- Antibiotics: For H. pylori infection (e.g., amoxicillin, clarithromycin, metronidazole).
- Cytoprotective Agents: Protect the stomach lining (e.g., sucralfate).
2. Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
- Avoid Triggers:
- Spicy, acidic, or fatty foods.
- Alcohol, caffeine, and carbonated drinks.
- Eat Smaller, Frequent Meals:
- Reduces pressure on the stomach.
- Quit Smoking:
- Smoking increases stomach acid production and delays healing.
- Manage Stress:
- Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
3. Treat Underlying Causes
- H. pylori Infection: Complete the prescribed antibiotic course.
- Medication-Induced Gastritis: Switch to alternative medications (e.g., acetaminophen instead of NSAIDs).
- Autoimmune Gastritis: May require vitamin B12 injections if deficient.
Home Remedies
- Ginger Tea: Soothes the stomach and reduces inflammation.
- Chamomile Tea: Calms the digestive system.
- Probiotics: Found in yogurt or supplements, they promote gut health.
- Aloe Vera Juice: May help reduce stomach inflammation.
When to See a Doctor
- If symptoms persist for more than a week.
- If you experience vomiting blood or black, tarry stools.
- If you have severe abdominal pain or unexplained weight loss.
Prevention
- Limit NSAID Use: Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest time.
- Avoid Alcohol and Smoking.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques regularly.
Key Points
- Gastritis is inflammation of the stomach lining, often caused by H. pylori, medications, or lifestyle factors.
- Treatment involves medications, dietary changes, and addressing the underlying cause.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications like ulcers or stomach bleeding.
If you suspect you have gastritis, consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and management.
- Tags:
- Gastritis, ជំងឺរលាកក្រពះ



