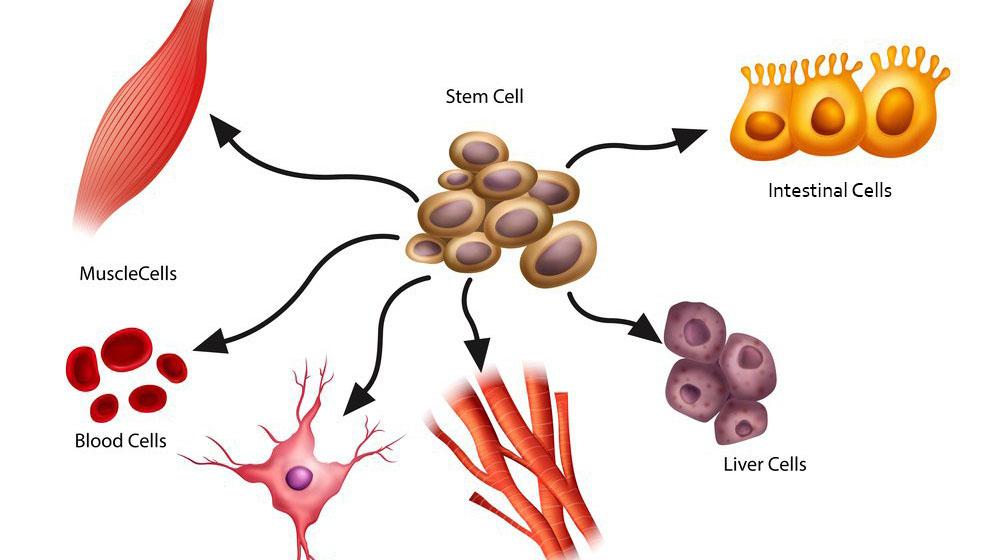
- Self-renewal means cells can also be continual their division for the stem cell.
- Remaining in the undifferentiated state
- Differentiation potential to be a specialized cell
Sources of Adult Stem Cell
Normally, stem cells can be found in every part of the body. They responsible on repairing the damaged cells or replacing the death cells. The growing of hair and nail also the construction of stem cells. However, in difference part of the body, different types and number of stem cells are found. The following list is the sources where stem cells can be found more than other places.
- Cord Blood
- Skin
- Peripheral Blood
- Placenta and umbilical cord
- Adipose tissue
- Baby teeth
- Liver
Cord Blood
Cord blood is an enriched source of Hematopoietic stem cell where Small number of T Cells can be found. A matter in number of T cells would lower the risk of GvHD (Graft versus Host Disease). However, there is only limited amount of approx. 80-200 ml in each umbilical cord depending on the pregnancy term and weight of infant. The amount from the collection also affected by the skill of collector and other risks such as placenta previa. The collection during the delivery can be done either before or after the separation of the cord.The good point on transplantation of cord blood is the restriction on HLA typing for allogenic usage could allow matching error for 2 decimal points. If necessary, 3 decimal points can be approved via doctor’s consideration.
Peripheral Blood Stem Cell
Peripheral blood is biggest source for all types of stem cell therefore the collection which can be done intravascularly has been developed more than from other sources. To increase ability on harvesting, G-CSF (Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor) or GM-CSF (Granulocyte Microphang Colony Stimulating Factor) could be injected subcutaneously 4 days before the collection via Apheresis machine. (Normally G-CSF works better than GM-CSF) There are an important caution on the usage of G-CSF. If number of white blood cells raise higher than 35×10 9L then should consider reduce G-CSF given and stop if raise up to 50×10 9L.Stem cells harvest from peripheral blood normally enough for the usage. There are also an enriched source of T Cells which would result on the restriction on HLA typing of 6 decimal points for allogenic usage.
Adipose Tissue
An enrich source of Mysenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) which is around 5%. To get MSC from adipose tissues normally uses enzyme to digest other cells then will be processed in centrifuge for the separation.MSC is the earlier stage of Ectoderm and Mesoderm which mean MSC can transform themselves to any cells categorised in both groups. The experiments have been trying for treatment of human nerves system, using MSC on repairing of neuron which developed from the cells in ectoderm. However, the usage of MSC for the cells developed from mesoderm such as bone and its joint, tendon
Baby Teeth
Another source that we can find stem cell is 6 front of the baby teeth and the wisdom teeth. Stem cells harvesting from teeth can be done approx. 48-72 after they are removed and simply place them in an instant kit. However, if the instant kit has not been prepared, the teeth might be soaking in unflavored milk then keep them at 4°C. For the laboratory processes of separation can be done using the same principle with Adipose tissue. For the teeth, bone area will be disintegrated, only nerve inside pulp cavity is where a small number of MSC are found. Therefore after the harvesting, those stem cells from teeth need to go through the laboratory for their nutrition to stimulate and transplantation to increase number of cells
Stem Cells from other sources
Keep eyes on interesting sources such as infant’s liver, skin, cord, Wharton’s jelly and amniotic fluid where they referred to many interesting experiments. For example, the transformation of the stem cell from skin to cornea or the treatment for repairing the vocal fold.
Characteristics of Regenerative Cell
- Homing: ability to travel to where cells were infected or needed of the repairing or replacing.
- Differentiation: the ability to transform to the specific cells
- Trophic support : ability of secretion different kind of substances such as Cytokine and Growth factor for tissue regenerative.
- Anti-inflammation: ability to reduce the inflammation.
- Neo-vascularization: ability to secrete important growth factors for the new blood vessels and solve the problems about scar tissue
- Anti-apoptosis: ability to reduce the number of death cells in the area
Treatment areas could affect the collection and the transplantation of stem cells. Even the treatments are for the same lesions could give various results which mean all factors surrounding the area of treatment are highly sensitive to the cells and require maximum care in the method of treatments even those treatments are for the same disease. These are the reasons attract worldwide attention to continuously develop with so many researches and clinical trials are going for all types stem cell’s treatments. However, in whatever way the treatments are done, controlling in the way of autologous is still the safest way for all living species.
For more info please click here
 Since Stem Cell was introduced in 1961. It was the important discovery on the repairing and replacing died or damaged cells which applied the similarities to all living species. The enormous expectations on stem cells of extending human lives become more and more realistic. This article will introduce us to different kinds of stem cells, its characteristic, development processes, the potential benefits and its sources.
Since Stem Cell was introduced in 1961. It was the important discovery on the repairing and replacing died or damaged cells which applied the similarities to all living species. The enormous expectations on stem cells of extending human lives become more and more realistic. This article will introduce us to different kinds of stem cells, its characteristic, development processes, the potential benefits and its sources.